Transforming Waste Into Value: A Comprehensive Exploration Of Waste Management And Resource Recovery
Transforming Waste into Value: A Comprehensive Exploration of Waste Management and Resource Recovery
Related Articles: Transforming Waste into Value: A Comprehensive Exploration of Waste Management and Resource Recovery
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Transforming Waste into Value: A Comprehensive Exploration of Waste Management and Resource Recovery. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Transforming Waste into Value: A Comprehensive Exploration of Waste Management and Resource Recovery

The world’s growing population and burgeoning consumption patterns have led to an unprecedented surge in waste generation. This presents a formidable challenge to our planet’s sustainability, demanding innovative solutions to manage waste effectively and responsibly. While waste disposal remains a crucial aspect, the focus is increasingly shifting towards resource recovery, a practice that transforms discarded materials into valuable resources, minimizing environmental impact and promoting circular economy principles.
This exploration delves into the multifaceted realm of waste management and resource recovery, examining the diverse approaches employed to extract value from waste. It highlights the crucial role of waste reduction, recycling, composting, and energy recovery in mitigating environmental harm and fostering sustainable development.
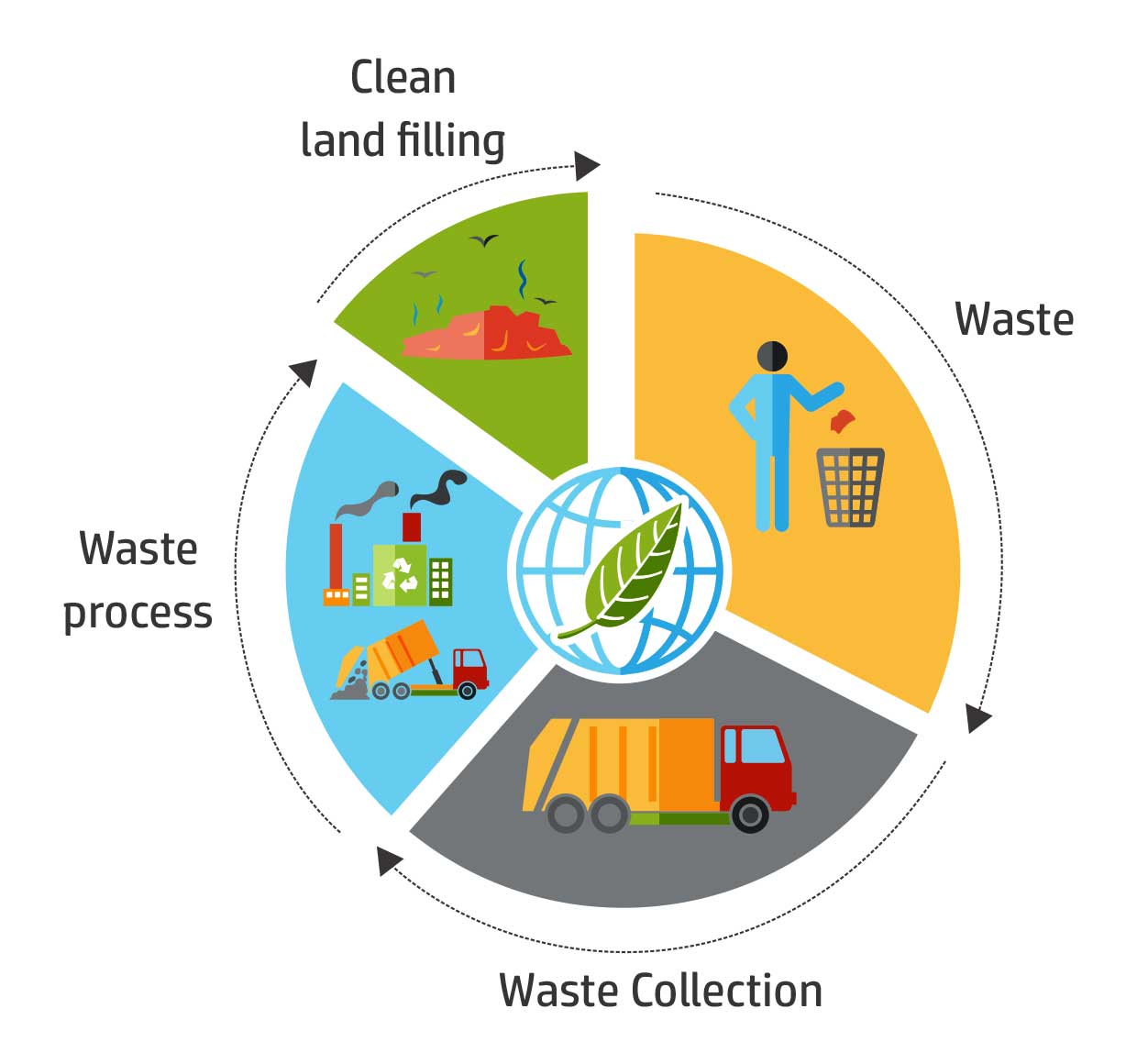
Understanding the Waste Hierarchy: A Framework for Sustainable Waste Management
The waste hierarchy, a cornerstone of sustainable waste management, provides a framework for prioritizing waste management practices. It emphasizes a sequential approach, starting with the most desirable option and progressing towards less desirable alternatives:
-
Prevention: Minimizing waste generation at the source is the most effective strategy. This involves reducing consumption, promoting reusable products, and adopting sustainable practices in manufacturing and packaging.
-
Reuse: Giving discarded items a new purpose extends their lifespan and reduces the demand for new resources. This can involve repairing, repurposing, or donating items.
-
Recycling: Processing used materials into new products conserves natural resources and reduces pollution. This involves collecting, sorting, and transforming materials like paper, plastic, glass, and metals.
-
Composting: Decomposing organic waste like food scraps and yard waste creates nutrient-rich compost, a valuable soil amendment for agriculture and gardening.
-
Energy Recovery: Extracting energy from waste through processes like incineration and anaerobic digestion provides a renewable energy source and reduces landfill volume.
-
Disposal: Landfilling, the least desirable option, involves burying waste in designated areas. This approach should be minimized, as it consumes valuable land and poses risks of pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
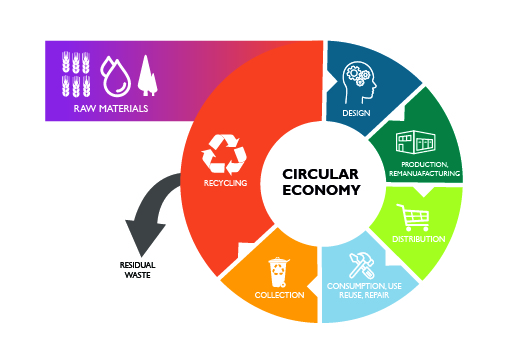
Resource Recovery: Extracting Value from Discarded Materials
Resource recovery, a key component of the waste hierarchy, involves extracting valuable materials or energy from waste. This practice encompasses a wide range of technologies and approaches, each tailored to specific waste streams:
1. Recycling:
-
Mechanical Recycling: This involves physically separating and processing materials like paper, plastic, glass, and metals to create new products. The process often involves sorting, shredding, washing, and melting.
-
Chemical Recycling: This approach uses chemical processes to break down polymers into their original monomers, which can then be used to create new plastics. This offers a promising solution for recycling complex plastic mixtures.
2. Composting:
-
Aerobic Composting: This involves decomposing organic waste in the presence of oxygen, using microorganisms to break down materials into nutrient-rich compost.
-
Anaerobic Digestion: This process breaks down organic waste in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas (methane) and digestate, a valuable fertilizer.
3. Energy Recovery:
-
Incineration: This process involves burning waste at high temperatures to generate heat and electricity. While effective in reducing waste volume, incineration raises concerns about air pollution and the potential for hazardous byproducts.
-
Gasification: This process converts waste into a combustible gas, syngas, through controlled heating in the absence of oxygen. Syngas can be used as fuel for electricity generation or other industrial processes.
-
Pyrolysis: This method involves heating waste in the absence of oxygen to produce solid, liquid, and gaseous products. The solid product, biochar, can be used as a soil amendment or fuel, while the liquid and gaseous products can be further processed for energy or chemicals.
The Importance of Resource Recovery: A Multifaceted Impact
The benefits of resource recovery extend beyond environmental protection, encompassing economic and social dimensions:
1. Environmental Benefits:
-
Reduced Landfill Dependence: Resource recovery significantly reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills, extending landfill lifespan and minimizing environmental risks associated with landfill leachate and greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Conservation of Natural Resources: Recycling and reuse conserve valuable resources like timber, minerals, and fossil fuels, reducing the need for extraction and processing, which often have significant environmental impacts.
-
Reduced Pollution: Resource recovery processes can reduce air, water, and soil pollution associated with waste disposal and resource extraction.
2. Economic Benefits:
-
Creation of New Industries: Resource recovery fosters the development of new industries focused on waste collection, sorting, processing, and product manufacturing, creating jobs and stimulating economic growth.
-
Resource Value Recovery: Transforming waste into valuable resources generates revenue, offsetting the costs of waste management and creating a more circular economy.
-
Increased Resource Security: Resource recovery enhances national resource security by reducing dependence on imported raw materials and fostering a more sustainable and resilient supply chain.
3. Social Benefits:
-
Improved Public Health: Reducing waste and pollution associated with waste disposal contributes to improved public health and well-being.
-
Community Engagement: Resource recovery initiatives often involve community participation, promoting environmental awareness and fostering a sense of responsibility.
-
Social Equity: Resource recovery can create job opportunities in disadvantaged communities, promoting social inclusion and economic empowerment.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Resource Recovery
Q: What are the challenges associated with resource recovery?
A: Implementing effective resource recovery programs faces several challenges, including:
-
Cost of Infrastructure and Technology: Setting up and maintaining resource recovery facilities requires significant investment in infrastructure and technology.
-
Market Demand for Recycled Materials: The success of recycling programs depends on market demand for recycled materials. Fluctuations in demand and the availability of virgin materials can impact the economics of recycling.
-
Contamination of Waste Streams: Recycling processes can be hindered by contamination from non-recyclable materials. Effective waste sorting and education are crucial to ensure the quality of recycled materials.
-
Public Awareness and Participation: Public awareness and participation are essential for the success of resource recovery programs. Education and incentives are needed to encourage proper waste sorting and reduce contamination.
Q: What are the future trends in resource recovery?
A: The future of resource recovery is marked by innovation and technological advancements:
-
Advanced Sorting Technologies: Artificial intelligence and robotics are being incorporated into sorting processes, improving efficiency and accuracy.
-
Chemical Recycling and Upcycling: Chemical recycling and upcycling technologies are gaining traction, offering new possibilities for transforming complex waste streams into valuable products.
-
Bioplastics and Bio-based Materials: The development of bioplastics and bio-based materials is creating alternatives to conventional plastics, promoting a more sustainable and circular economy.
-
Waste-to-Energy Technologies: Advanced waste-to-energy technologies are being developed, improving energy efficiency and reducing environmental impacts.
Tips for Promoting Resource Recovery
1. Reduce Waste Generation: Minimize waste at the source by reducing consumption, choosing reusable products, and adopting sustainable practices.
2. Sort Waste Properly: Follow local guidelines for waste sorting and ensure that recyclable materials are free from contamination.
3. Compost Organic Waste: Compost food scraps and yard waste to create valuable soil amendment and reduce landfill volume.
4. Support Local Recycling Initiatives: Participate in local recycling programs and advocate for policies that promote resource recovery.
5. Choose Products Made from Recycled Materials: Opt for products made from recycled materials to support the circular economy and reduce demand for virgin resources.
Conclusion: Towards a Circular Future
Resource recovery is not merely a technological endeavor; it is a fundamental shift in our relationship with resources. By embracing the principles of the waste hierarchy and adopting innovative solutions for resource recovery, we can transform waste from a liability into a valuable asset. This transformation will not only mitigate environmental harm but also create economic opportunities, enhance social well-being, and pave the way for a more sustainable and circular future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Transforming Waste into Value: A Comprehensive Exploration of Waste Management and Resource Recovery. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Shaping The Homes Of Tomorrow: Home Decor Trends For 2025
- Navigating The Evolving Landscape Of Home Decor Trends: A Comprehensive Guide
- Weaving History And Home: A Guide To Unique Vintage Farmhouse Decor
- The Enduring Appeal Of Wooden Duck Home Decor: A Timeless Symbol Of Nature And Serenity
- Beyond The Ordinary: A Guide To Unique Home Decor Accessories
- Navigating The Fast Fashion Landscape: Exploring Alternatives To SHEIN
- A Global Network Of Home Improvement: The Reach Of The Home Depot
- Finding The Perfect Pieces: A Guide To Home Decor Shopping

Leave a Reply