The Cloud: A Comprehensive Exploration Of Modern Computing
The Cloud: A Comprehensive Exploration of Modern Computing
Related Articles: The Cloud: A Comprehensive Exploration of Modern Computing
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Cloud: A Comprehensive Exploration of Modern Computing. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Cloud: A Comprehensive Exploration of Modern Computing

The phrase "on cloud nine" evokes a sense of joy and contentment, but in the realm of technology, "the cloud" signifies a revolutionary shift in how we access and utilize computing resources. This article delves into the multifaceted world of cloud computing, explaining its core concepts, benefits, and implications for individuals and organizations alike.
Understanding the Cloud: Beyond the Metaphor
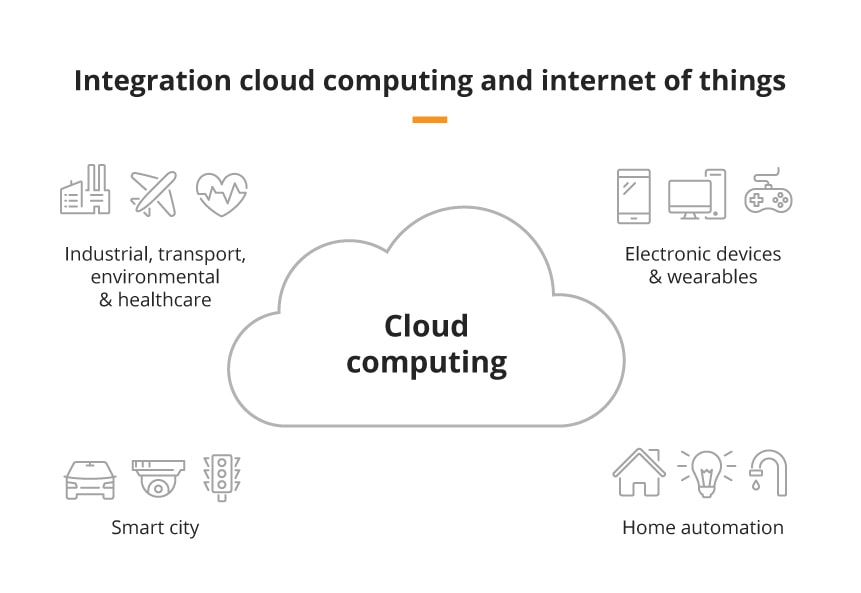
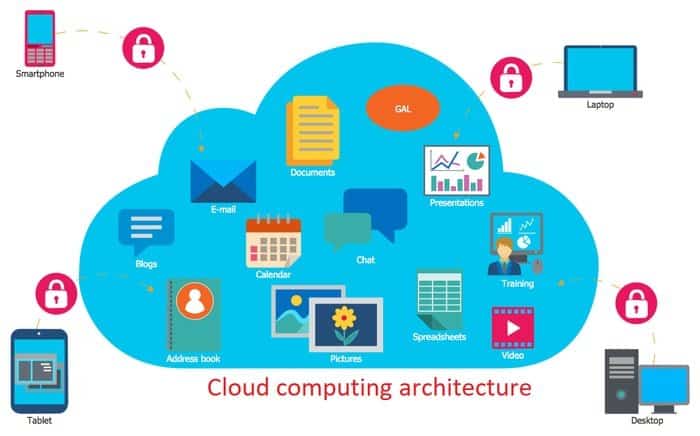
The cloud is not a physical entity, but rather a network of interconnected data centers and servers. These servers are owned and operated by third-party providers, offering a wide range of computing services to users over the internet. Imagine a vast, interconnected web of powerful computers, accessible at any time, from anywhere. This is the essence of cloud computing.
The Core Pillars of Cloud Computing:
-
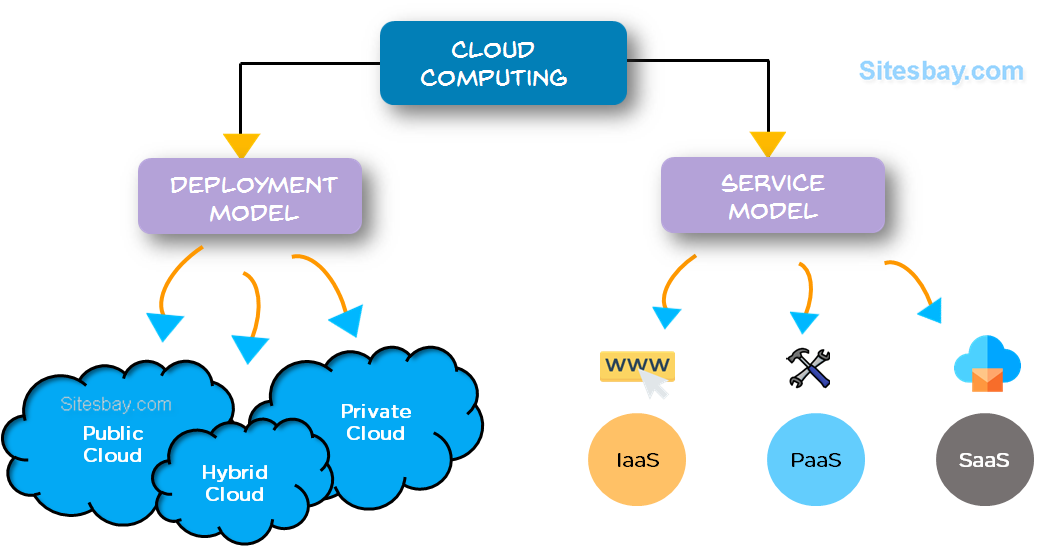
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This foundational layer provides the basic building blocks of computing, such as servers, storage, and networking. Users can rent these resources on demand, scaling up or down as needed. Think of it as renting a virtual computer, complete with its own operating system and storage space.
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS): This layer offers a platform for developing and deploying applications. It includes tools, services, and frameworks that streamline the development process, allowing developers to focus on building applications rather than managing infrastructure.
-
Software as a Service (SaaS): This top layer provides readily available software applications, accessible through a web browser or mobile app. Examples include email services (Gmail), productivity suites (Google Workspace), and project management tools (Asana).
Benefits of Cloud Computing:
-
Cost-effectiveness: By eliminating the need for expensive hardware and infrastructure investments, cloud computing offers significant cost savings. Users pay only for the resources they consume, making it an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
-
Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud services can be scaled up or down instantly to meet changing demands. This flexibility allows businesses to respond quickly to market fluctuations and unforeseen events.
-
Accessibility and Collaboration: Cloud-based services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering collaboration and remote work. Teams can work together on projects seamlessly, regardless of their physical location.
-
Enhanced Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures to protect sensitive data. Their expertise and resources often exceed those available to individual organizations, offering a higher level of security for data storage and processing.
-
Innovation and Agility: Cloud computing empowers organizations to experiment with new technologies and applications without significant upfront investment. This agility allows for rapid innovation and quicker time-to-market for new products and services.
Types of Cloud Deployment Models:
-
Public Cloud: Services are provided by a third-party provider, accessible to anyone over the internet. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
-
Private Cloud: Services are dedicated to a single organization, hosted within their own data center or a managed facility. This provides greater control over data and security.
-
Hybrid Cloud: A combination of public and private cloud services, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of both models. This approach provides flexibility and cost optimization.
Implications of Cloud Computing:
-
Shifting Business Models: Cloud computing has fundamentally changed how businesses operate. Organizations are moving away from traditional on-premise infrastructure towards cloud-based solutions, leading to a more agile and cost-effective approach.
-
Rise of the Digital Workforce: The accessibility and collaborative nature of cloud services have enabled the rise of remote work and distributed teams. This has created a more flexible and diverse workforce, opening up new opportunities for individuals and businesses.
-
Data-Driven Decision Making: Cloud computing provides access to vast amounts of data, enabling organizations to gain valuable insights and make data-driven decisions. This has revolutionized business analytics and decision-making processes.
FAQs about Cloud Computing:
Q: Is cloud computing secure?
A: While cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, security is a shared responsibility. Users must implement strong passwords, enable multi-factor authentication, and follow best practices for data protection.
Q: What are the risks of using cloud computing?
A: Potential risks include data breaches, service outages, and vendor lock-in. It is crucial to choose reputable providers with robust security measures and to have a disaster recovery plan in place.
Q: How do I choose the right cloud provider?
A: Consider factors such as cost, scalability, security, compliance requirements, and the provider’s track record. Evaluate the services offered and ensure they align with your specific needs.
Q: What are some examples of cloud-based applications?
A: Popular examples include email services (Gmail), productivity suites (Google Workspace), project management tools (Asana), CRM systems (Salesforce), and cloud storage services (Dropbox).
Tips for Implementing Cloud Computing:
-
Start Small: Begin by migrating non-critical applications or workloads to the cloud. This allows you to test the platform and gain experience before moving larger applications.
-
Choose the Right Provider: Evaluate different cloud providers and choose one that aligns with your business needs and budget.
-
Develop a Cloud Strategy: Define your cloud adoption goals, identify potential use cases, and develop a roadmap for migration.
-
Focus on Security: Implement strong security measures and follow best practices to protect your data.
Conclusion:
Cloud computing has fundamentally transformed the way we access and utilize computing resources. It has become a ubiquitous force, empowering individuals and organizations to achieve greater efficiency, scalability, and innovation. By understanding the core concepts, benefits, and implications of cloud computing, individuals and businesses can harness its power to drive growth and success in the digital age.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Cloud: A Comprehensive Exploration of Modern Computing. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Shaping The Homes Of Tomorrow: Home Decor Trends For 2025
- Navigating The Evolving Landscape Of Home Decor Trends: A Comprehensive Guide
- Weaving History And Home: A Guide To Unique Vintage Farmhouse Decor
- The Enduring Appeal Of Wooden Duck Home Decor: A Timeless Symbol Of Nature And Serenity
- Beyond The Ordinary: A Guide To Unique Home Decor Accessories
- Navigating The Fast Fashion Landscape: Exploring Alternatives To SHEIN
- A Global Network Of Home Improvement: The Reach Of The Home Depot
- Finding The Perfect Pieces: A Guide To Home Decor Shopping
Leave a Reply